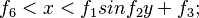$triregionnumber
The number of regions that is in the triangular shape.
Example
$triregionnumber 2
This means that there are two triangular regions. This command must be set after the command
$ranges. The "triregionnumber" must be smaller than the "range number".
This command needs to be set before the command before the commands $triregiontype, $triranges,
For example:
$triregionnumber 2
$triregiontype @type @periodnumber @period_spacing @type @periodnumber @period_spacing
$triranges @f1 @f2 @f3 @f4 @f5 @f6 @f1 @f2 @f3 @f4 @f5 @f6
@f1 @f2 @f3 @f4 @f5 @f6 are defined below according to its type For the @type, it is the same definition as type in $emptyperiodshape, see below For @periodnumber, it is repeating how many times For the @period_spacing, it is defining the spacing of each repeating objects.
Example of @type
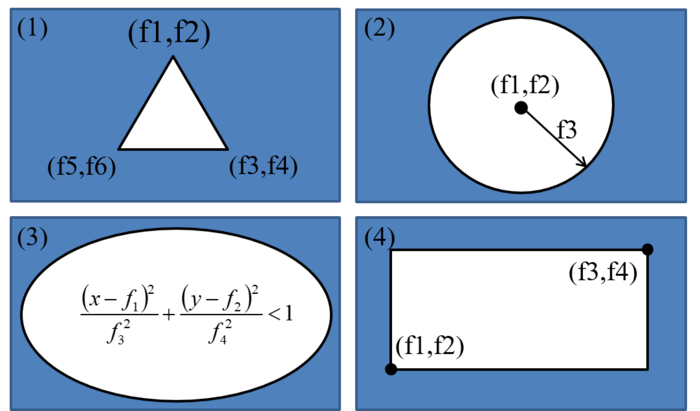
@type.1~4 are triangle, circle, ellipse and rectangle.
@type = 1 is triangle. If it have n-trianges, it it repeating along x direction.
@type = 11 is triangle. If it have n-trianges, it it repeating along y direction.
@type = 2 is circle. If it have n-circles, it it repeating along x direction.
@type = 21 is circle. If it have n-circles, it it repeating along y direction.
@type = 3 is ellipse. If it have n-ellipses, it it repeating along x direction.
@type = 31 is ellipse. If it have n-ellipses, it it repeating along y direction.
@type = 4 is rectangle. If it have n-rectangle, it it repeating along x direction.
@type = 41 is rectangle. If it have n-rectangle, it it repeating along y direction.
If the parameters are not show in the figure, you should set those parameters as 0.
Type5~8 are sine shape period structure.
Type.5 and 6 can be determined by this expression:
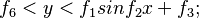
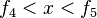
Type.7 and 8 can be determined by this expression: